Главная
страница
Сведения об авторах
WASTE WATER PRE-CONDITIONING FOR ODOUR AND CORROSION MINIMIZATION
Frechen F.-B., Franke W., Romaker J., Kassel University, Kassel, Germany
Sewer systems could produce odorous emissions in case of odorous inlets or if waste water gets under anaerobic conditions, for example in pressure lines. In both cases a waste water pretreatment could help to minimize the odorous emissions from the sewer as well as the corrosion potential of sewer air, as many people have published before. In order to keep the conditioning economical interesting, a measurement of application success is needed, what is until today no standard.
In a first case study monitoring of the success of dozing two different Ca(NO2)3 agents at pressure line will be shown. Aim in this case was the minimization of H2S in sewer air in the pressure less sewer after the end of the pressure line. It will be shown, how a strategy for a dozing optimization can be performed with the use of daily variation curves of flow and loads. The frequencies of H2S concentrations during different measurement periods are given in Fig. 1.
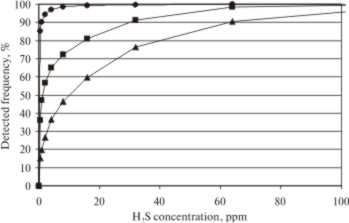
Fig. 1. Success of dozing Ca(NO2)3 measured via H2S
minimization:
![]()
In a second study success monitoring of dosing FeCl2 at a large municipal sewer to minimize odour and H2S will be show. Odour gets monitored by random sampling of sewer air (olfactometric analysis according to DIN EN 13725) and water (odour emission capacity according to FRECHEN and KО..STER). H2S in sewer air is investigated with gas monitors. S2- in liquid phase is analysed with the help of a self developed semi online sampling device functioning similar to DIN 38405-27, the device is shown in Fig. 2.
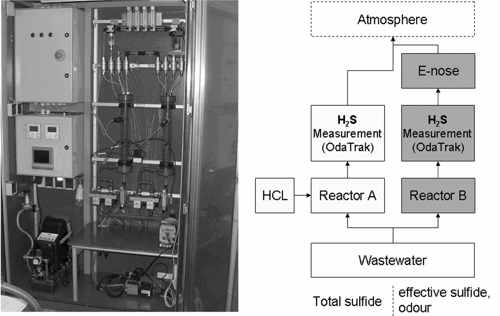
Fig. 2. Sulphide measurement device
Until 2008 the device will be equipped with a multi
sensor array analyser to detect odour, too. This optimization aims on an
online-monitoring with feedback to the dosing stations and seems to be
interesting for large sewer system application. Because H2S is
responsible for biogenic corrosion a minimization of H2S improves the
corrosion situation in a sewer, too.
Frechen Franz-Bernd, Prof., Department of
Sanitary and Environmental Engineering, Kassel University, Kurt-Wolters-Str. 3,
Kassel, 34125, Germany. Tel. (561) 804-39-91
Franke Wolfram, Dipl.-Ing., Department of Sanitary and Environmental
Engineering, Kassel University, Kurt-Wolters-Str. 3, Kassel, 34125, Germany.
Tel. (561) 804-39-91. E-mail
Romaker Jan, Dipl.-Ing., Department of Sanitary and Environmental
Engineering, Kassel University, Kurt-Wolters-Str. 3, Kassel, 34125, Germany.
Tel. (561) 804-39-91
© Независимое агентство экологической информации
Последние изменения внесены 19.09.08